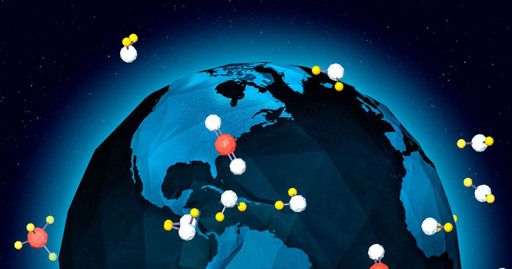
There’s a simple story of the greenhouse effect: A blanket of carbon dioxide envelops the planet, letting sunlight in but trapping its heat. As a result, Earth warms. But how does this actually work? Carbon dioxide amounts to only a tiny smattering of gas molecules — 0.042%, or roughly 420 parts per million — in our thick atmosphere. And yet, we know that doubling carbon dioxide levels can…
From Quanta Magazine via this RSS feed
You must log in or # to comment.