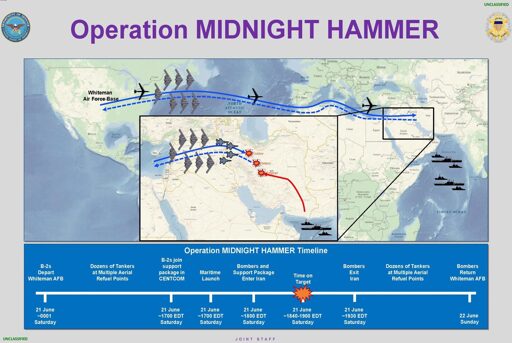
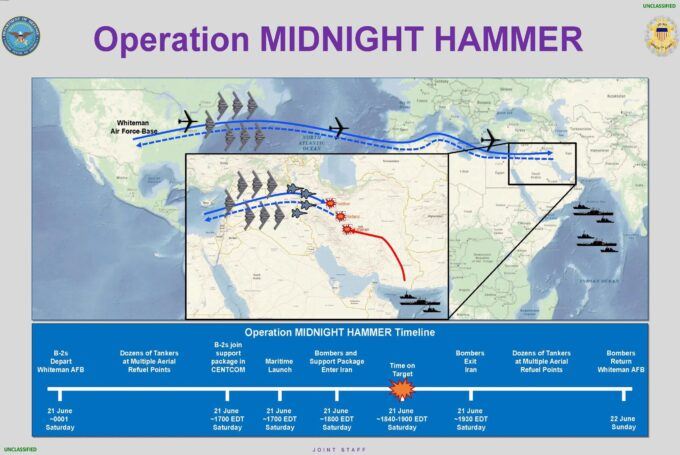
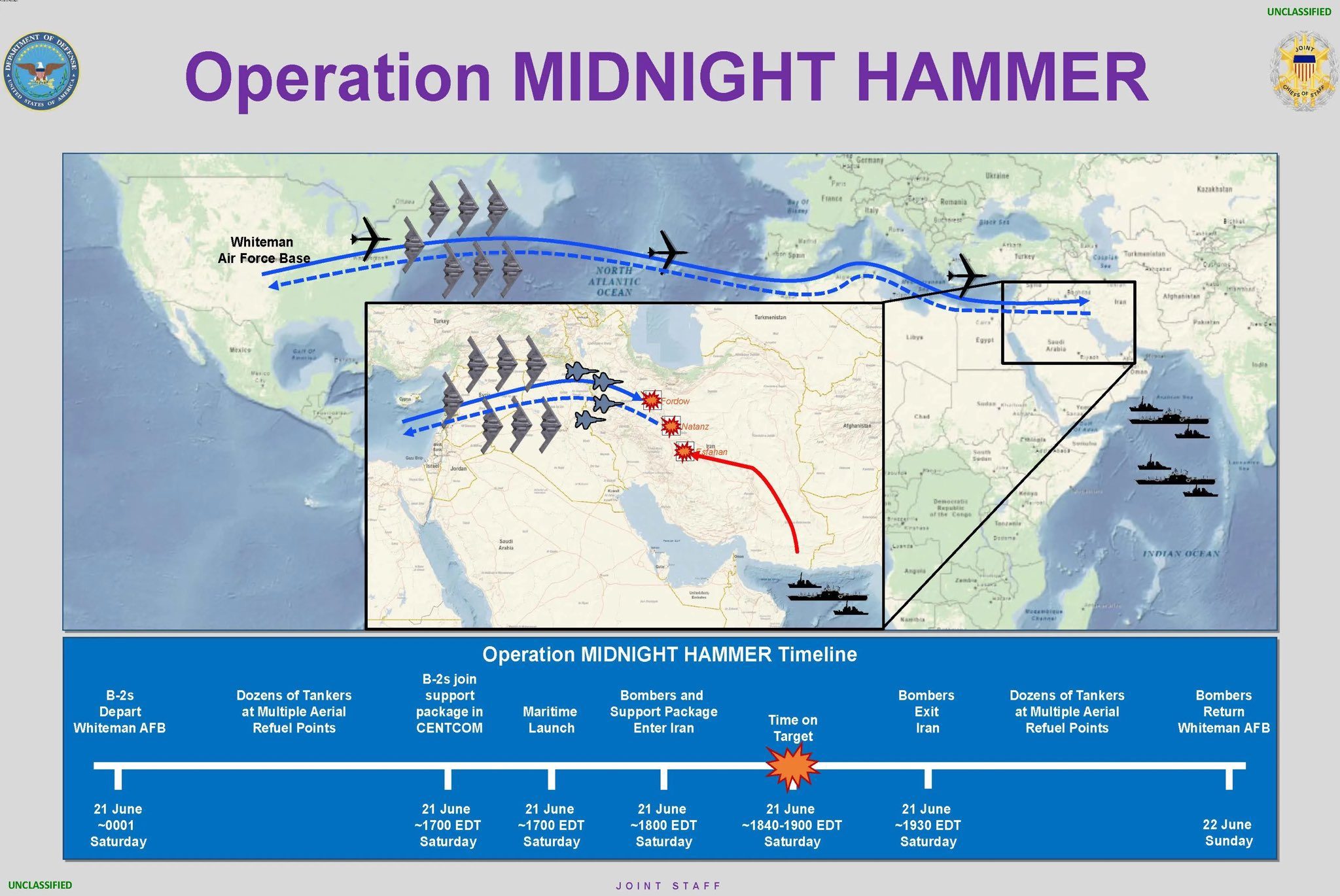
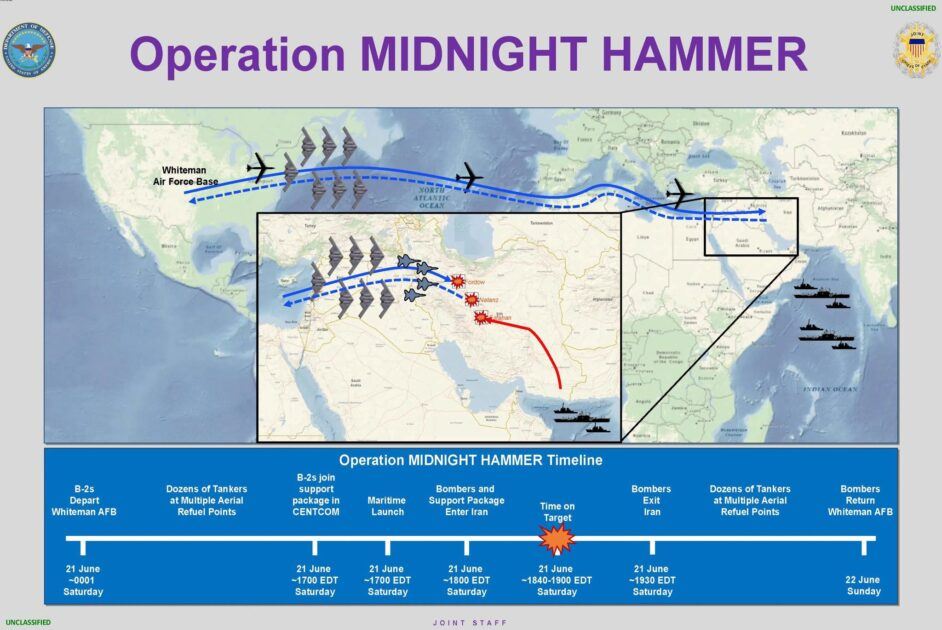
Timeline of Operation Midnight Hammer – Public Domain
With the bombing of Iran’s nuclear sites at Natanz, Isfahan, and Fordow, the United States risked becoming “plugged … into some of the fiercest conflicts in the world,” according to veteran Middle East correspondent Patrick Cockburn. The ceaseless refrain—repeated by Prime Minister Netanyahu in his latest tirade at the UN General Assembly, “the curse of Iran’s terror axis”—“constitutes the most awesome threat not only to Israel, but to U.S. interests in the region, means that Trump is now directly involved “not only against Iran, but in interlinked conflicts” against Hamas, Hezbollah, the Houthis, and various Shiite paramilitary groups aligned with Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps in Iraq. Should the Islamic Republic choose to retaliate against American troops stationed in the vicinity of its reach, the U.S. will not interpret it as an overdue moment of reckoning for its years of nihilistic endeavors—it will treat it as yet another unprovoked offensive. Key to the expansion of their power and territory, violent states are largely in the business of exploiting pretexts, manipulating or even fabricating threats that justify intervention and subjugation. The new phase of the conflict against Iran thus carries all the foul trappings of a “forever war,” in which the stated objectives admittedly cannot be attained, and withdrawal is considered a humiliating capitulation that haunts electoral success. Trump’s patented volatility could prevent this outcome, but that would require a decoupling of Iran from the conflicts raging in the Arab states.
The timing was telling. As Iran’s Foreign Minster Araghchi met with European leaders in Geneva, who counseled the Islamic Republic to call off the bombing of Israel and accept U.S. demands to relinquish all uranium enrichment, Israel was pummeling Tehran. Pressure was being exerted on all fronts, but the professed goal of preventing the Iranian regime from developing nuclear weapons suffers from a fundamental incoherence: the more violent these preventive efforts become, the more likely it is that Iran will move to weaponize its nuclear energy. Although current assessments, from the IAEA to Tulsi Gabbard, conclude that it has been over two decades since Iran pursued such a program, figures in both Israel and the U.S. insist on a repetition of previous debacles. “The world has witnessed how the United States attacked Iraq for, as it turned out, no reason at all,” wrote Israeli military historian Martin Van Creveld in August 2004. “Had the Iranians not tried to build nuclear weapons, they would be crazy.” A 2012 article by the late Kenneth Waltz that caused quite a stir proposed that, “Despite a widespread belief to the contrary, Iranian policy is not made by ‘mad mullahs’ but by perfectly sane ayatollahs who want to survive just like any other leaders.” If the regime “desires nuclear weapons, it is for the purpose of providing for its own security, not to improve its offensive capabilities (or destroy itself).”
“Iran doesn’t want to speak to Europe,” Trump said during the Geneva proceedings. “They want to speak to us. Europe is not going to be able to help on this one.” Consistent with U.S. positions taken in the past, European involvement in this region can serve only two purposes: one, to effectively communicate U.S. demands in its stead; and two, to provide a veneer of multilateral legitimacy, assuaging the world community whenever it feels that the U.S. is exercising outsized influence in negotiations. One 1999 EU resolution following the Wye Memorandum negotiations, for example, lamented that “despite the fact that it continues to be the leading supplier of economic and financial assistance to the region, the European Union was not involved in the political discussions which led to the resumption of dialogue nor in the undertakings entered into”—a historical pattern that a handful of European states profess to have put behind them by recognizing the State of Palestine.
Iran’s exchange with Israel was largely a predictable culmination of the events stimulated by October 7, when Israel, in league with its ascendant American backers, seized upon “the worst massacre of Jews since the Holocaust (Jonathan Greenblatt)” and began implementing their contingency plans for Gaza. From the U.S. and Israel’s point of view, Tehran constitutes the final domino required to fall in a series of four: first, the leadership of Hamas, having orchestrated the bloody 2023 break-out from the Gaza Strip, what senior Israeli national security official Giora Eiland labeled in 2004 as a “huge concentration camp,” the kill-list of Deif, Haniyeh, and Sinwar graciously prepared by the International Criminal Court in the form of arrest warrants; second, the leadership of Hezbollah, whose subsequent intervention on behalf of the Palestinians led to the decimation of its own leadership and command structure, while producing a deep trepidation among fellow Lebanese to become embroiled in more war with Israel; third, the rapid undoing of the Assad regime in Syria, ending not only the gross depredations of that family’s dynasty, but also the primary land-route through which Iran could militarily bolster its Arab allies.
Posing as the arbiter of maturity and wisdom, The New York Times’ editors recently opined that, before “being dragged into another war in the Middle East,” which would entail “committing American blood and treasure,” Trump and his retinue of extraordinary legal scholars mustn’t forget to “put the issue to a vote in Congress,” so as not to violate the canons of domestic checks and balances and hence repeat the mistakes of our past. After all, “Our laws are explicit on this point.” To declare war “is not the decision of Mr. Netanyahu or Mr. Trump. Under the Constitution, Congress alone has that power.” With this prudent admonition, the editors confess that, of course, “Iran’s government is a malevolent force in the world and that it has made substantial progress toward acquiring a nuclear weapon,” but “thanks partly to Israel’s humbling of Iranian proxies like Hamas and Hezbollah,” there may be another way by which the beast can be subdued. No mention is made, as part of this liberal civics review, of the flagrant illegality of Israel’s bombing of Iran, its ongoing genocidal project in Gaza, the conduct of its “humbling” of Arab foes, or of U.S. complicity in it all, the last of which proceeds with a multi-dimensional criminality designated only for the most powerful international gangsters.
Sentiments such as this, rich in both entitlement and fatuity, elicit ridicule in other, civilized intellectual cultures better acquainted with the injurious nature of Washington’s aggressions. Even in countries on the immediate periphery of those discussed above, having been (by and large) spared the tonnage of F-35 payloads and Abrams tanks, observers perceive new waves of U.S. bombing as little more than another stage in a trite imperial pattern, with perhaps still more devastating consequences than its previous incarnations. Aasim Sajjad Akhtar writes in Pakistan’s leading daily, Dawn, that, “There is no secret to what the Empire and its Israeli outpost want—to eliminate the one challenger to their power in the Muslim world,” all others having been effectively cut down or coopted. “If today the argument is that the repressive, theocratic regime that rules Iran must be removed, yesterday the same was said about the Afghan Taliban, Saddam Hussein, the Assad dynasty and Muammar Qadhafi.” Incidentally, at least three of those governments were destroyed under concocted pretexts that metamorphosed into loftier concerns over state repression. In the case of Pakistan, Akhtar explains, “Ziaul Haq and Pervez Musharraf immensely damaged Pakistani society by aligning with Washington to prosecute wars in Afghanistan,” the “enduring legacies” of which are “wide-spread influence of the militant right-wing, and the ‘Kalashnikov culture’” that has fueled Islamist insurgencies in the Balochistan region. Discussion of this prevailing maelstrom will remain vexingly absent from Western arguments favoring Iran’s destruction.
News reports claim that both Hezbollah and the Houthis have been ordered by their paymaster in Tehran to stand down for the time being, to be reactivated in the event of another U.S. escalation. Parties to the Axis of Resistance, however, understand well the illusory nature of such a stasis. Should Israel find itself itching for a fix, it will simply provoke a conflict with a target of its choosing, confident in the ability of the great revisionists of chronology in Western media to properly assign blame. Already, the media are warning of Iranian efforts to rearm its Axis, with numerous shipments of weapons reportedly intercepted en route to Lebanon and Yemen. All the while, Prime Minister Netanyahu has accused the al-Sharaa regime in Syria of crossing “red lines,” that is, inside Syria, one of which is sending troops to areas on the outskirts of the Golan Heights, illegally annexed to Israel. The utterly laughable pretext is the protection of the Druze minority of Syria, as if Israel has suddenly decided to balance its genocidal impulses in Gaza with purely altruistic ones in Syria. In fact, this “pledge to defend the group is giving [Israel] an opportunity to display military dominance over its weaker neighbor and assert more control over their shared border,” according to The Wall Street Journal.
President Obama’s special envoy to Iran, Robert Malley, summarized Israel’s current strategy to Adam Shatz as “the regionalisation of the ‘mow the lawn’ strategy practised in Gaza and Lebanon.” In Syria, he added, “it has gone beyond ‘mowing the lawn’ – it’s ‘mow the hell out of whatever dirt may still be there.’ Even without any evidence of a Syrian intent to attack, even in the presence of clear conciliatory signals from the al-Sharaa government, Israel has continued to go after supposed weapons caches and to occupy parts of southern Syria. They did this because they could, because Syria was in no position to lift a finger in response.” In this respect, Syria is the ideal punching bag, enduring abuse while clamoring for legitimacy.
This drive to provoke is tendentious in Israeli strategic operations, and the associated apologetics that define mainstream commentary likely affect the measurement and care with which rivals conduct their retaliatory maneuvers. In other words, in a thoroughly captured media environment, unprovoked strikes can be sold as acts of defense. A Chatham House analysis of last April’s Iranian bombing of Israel, retaliation for the latter’s attack on Iran’s embassy in Damascus that killed a senior commander of the IRGC, along with 15 others, found that, “Had Iran’s intent been to hurt Israel, it wouldn’t have violated a core principle of military operations – the element of surprise. But it did. It telegraphed its intentions to Washington and several Arab and European capitals, and assured them that its strike would be relatively limited,” resulting in minimal damage. Efforts to sell Iran’s later bombing of Tel Aviv and Haifa as more unprovoked aggression have fallen flat in most of the world, resulting in a worrying deficit of sympathy for Israel.
Historically, widely publicized atrocities have prompted Israel’s most ardent supporters to greatly accelerate their white-washing efforts. The first major debacle with which the lobby contended was the Qibya massacre of October 1953, when David Ben Gurion’s forces, led by a young Ariel Sharon, killed some 70 Palestinian civilians. The fallout was unexpectedly difficult, drawing rebuke from Washington. Isaiah Kemen, the Abraham Foxman of his day, conceded privately that the killings “undermined the moral position of the Jewish people … discredited the premises of our propaganda and has given the color of truth to Arab propaganda.” Israel’s 1982 invasion of Lebanon, and, later, Operation Cast Lead in 2008-9 resulted in similar international isolation.
Israel’s image as a blameless sanctuary for the Jewish people, surrounded by “human animals,” in the forthright phrase of Israel’s former Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, once benefited from a buoyancy rarely seen in world affairs, certainly for a state of its size. This was not achieved through standard techniques of Congressional lobbying. What cannot be denied is that the operative networks of the “Israeli Lobby” extend far beyond AIPAC, the ADL, or even the Christian Broadcasting Network. In fact, they encompass practically the whole spectrum of elite Western institutions, including the news media, scholarship, politics, the corporate sector, high-tech, entertainment, and finance. So awesome and reflexive are their defenses (and promotions, in the case of the American Evangelical community) of Israeli violence that widespread cynicism thrives as to whose bidding the U.S. government is actually doing.
Horrifying images of mothers holding withered children and mobs of incalculable Gazans struggling for food aid has evidently turned the tide of public opinion against Israel, once again. A July 2025 Gallup poll shows that, by now, only a minority of Americans approve of Israel’s military actions in Gaza, and a majority disapprove of its bombing of nuclear sites in Iran. The time is now ripe for the kind of reappraisal required to extend this disapproval. We need not accept the notion that U.S.-Israeli terror is the sole determinant in the remaking of the Middle East. Its obvious unpopularity can help give rise to an educational restructuring, in which all roads no longer lead to Iran. The task, of course, is a tall one.
Iran as Boogeyman
Svante Cornell, a Swedish scholar long known for his predilections for the Azeri dictatorship, bemoans the Iranian “arc of domination” in the neighboring Arab World, as it takes advantage of what he feels are the honest miscalculations of the U.S., particularly in Iraq. He alleges that the Bush administration, for example, bet on the wrong horse, falsely expecting that empowering its Shia majority would translate into democratic dividends and gratitude for having toppled its chief enemy, Saddam Hussein. “But,” Cornell says, “the U.S. Iraq war did not go according to plan, and the missteps of the U.S. opened an opportunity for Iran to step in and work not only to counter the U.S. presence in Iraq, but to assert its own influence in the vacuum created by the United States.” How utterly nonplussed Bush and his planners must have been at the frigid welcome they received in Iraq, one of many dramatic twists in the epic, Why Do They Hate Us? The real story of our “failure” in Iraq is therefore the industrious cunning of the mullahs, who thwarted another democratization effort. Bone-headed accounts such as this read much like the internal assessments of the Reagan era, couched in the purity and virtue of its own foreign policy. A 1983 intelligence memo declared that “Moscow has chosen to allow its relationship with three successive US Administrations to deteriorate in substantial measure because of its refusal to moderate its aggressive pursuit of Third World opportunities.” Like Russia before it, Iran today is not to cultivate allies, only obedience, and fold whenever the legitimacy of its power projection comes into doubt.
In one of the few in-depth studies of the event, Ervand Abrahamian writes in his history of the U.S. and Britain’s 1953 overthrow of Iran’s parliamentary regime that “the coup left a deep imprint on the country—not only on its polity and economy but also on its popular culture and what some would call mentality.” Governments the world over suffered similar fates throughout the 20th century, many of whom are yet to fully recover even after obtaining a degree of independence. Materially, continues Abrahamian, “the coup set back by at least two decades the whole process of oil nationalization throughout the world—especially in the Middle East and North Africa.” Along with converting the country into a vicious dictatorship that amassed one of the worst records of torture and political repression in the world, Iranians were not granted reprieve from the scramble for its oil resources. Eventually, the era of decolonization saw one victim after another begin to retake, or at least reorient the control of, its foreign-owned resources. Major producers slowly “took over their oil resources, and, having learned from the past, took precautions to make sure the oil companies would not return victorious.”
In the wake of the October 1973 war between Egypt and Israel, and the ensuing oil embargo, Henry Kissinger pioneered the method by which the excess petrodollars of the region’s major oil producers would be recycled into expensive capital-intensive projects procured by the West. The aim was to establish a multinational counter to the price-setting powers of the producers by setting up what analyst David Spiro called an “oligopsony,” or a “cartel of consumers.” “Large scale development projects and other projects will put the Shah, for example, in a position where he must sell oil in order to sustain the commitments he has made,” Kissinger told a group of congressmen in June 1975. Diplomatic historian Jacob Darwin Hamblin’s review of the record finds that “Nuclear power generation became a key part of that petroleum strategy” primarily to free up oil for lucrative sales on the international market. Assistance from Western institutions was crucial. Eager to begin feeding from the trough, “French negotiators convinced Iran to build its enrichment facility in France, and the decision turned out to be a serious blunder for Iran, tying up considerable sums of capital.” It ultimately proved “particularly good for France, which was able to secure its own enrichment future with external money, and have the facility at home, in the southern provincial village of Pierrelatte. Most importantly, the project absorbed an enormous amount of Iranian capital and gave France some leverage in its negotiations with Iran in any future oil crisis.” The arrangement quickly bore fruit. “We may have broken OPEC,” Kissinger positively reported to President Ford in March 1975.
Before long, Iranian authorities grew skeptical of this scheme and sought more independence in its quest for peaceful nuclear energy. Having ratified the Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) in 1970, Iran was legally entitled to produce on its own soil, access, and dispose of its nuclear energy as it saw fit, granted that it was for peaceful purposes. Breaking free of external control became a key rallying cry for the young protestors who eventually spearheaded the removal of the Shah. “The behavior of the United States reinforced Iranian desires for diversification in partnership,” says Hamblin, and, since the Islamic Revolution of 1979, to no one’s surprise, “Russia has been particularly helpful in picking up where Europeans left off,” providing technology and know-how on drastically different terms. In light of other changes in international political alignment, China has also become the primary purchaser of Iranian oil, particularly worrying because it “is too big for Trump to bully now,” as Bloomberg Businessweek has recently noted.
Little wonder why editors in the business press seem to want nothing more than to restore the pre-1979 system. Trump has wondered aloud why Iran would want to produce nuclear energy while in possession of so much oil, and many commentators now look forward to an agreement which would see it again import its enriched uranium, ostensibly from Western sources. Put differently, Iranian energy-independence would prove disastrous for U.S. control.
Throughout the 1990s, the reformist government of President Khatami suggested a track for negotiations aiming to resolve all the most pressing areas of antagonism, including “weapons of mass destruction, a two-state solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the future of Lebanon’s Hizbullah organisation and cooperation with the UN nuclear safeguards agency [IAEA],” as reported in the Financial Times in 2006. The EU urged that it be pursued, but was forced by the Clinton administration to fall in line and retreat. A similar situation followed the U.S.-British invasion of Iraq in 2003, when the U.S. similarly rebuffed Iran-EU efforts. In May 2010, with encouragement of the Obama administration, Turkey and Brazil offered to help mediate the growing impasse, proposing that Iran would export close to 1,2000 kg of its low-enriched uranium to France and Russia for conversion into civilian-grade fuel, after which it would be returned for its domestic industries. The next month, the U.S. killed it at the Security Council in the form of Resolution 1929, opting for more sanctions.
In a 2013 profile on the current Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei, specialist Akbar Ganji outlines a solid rationale that Iran could easily adopt, in light of the preceding 46 years of antipathy towards the Islamic Republic: “Khamenei suspects that even if all of Iran’s nuclear facilities were closed down, or opened up to inspections and monitoring, Western governments would simply pocket the concessions and raise other issues—such as terrorism, human rights, or Israel—as excuses for maintaining their pressure and pursuing regime change,” citing Libya’s Qaddafi and Saddam’s Iraq, who were still invaded after having relinquished their weapons of mass destruction. The regime still chose the path of negotiations, concluding with the 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, subject to the most rigorous sanctions regime in the world, hopeful sign for anyone worried about a threat from Iran. The E3, flouting Russian and Chinese efforts to salvage diplomacy, reimposed severe “snapback” sanctions in September that will further strangle the Iranian economy, in what is billed psychotically as another effort to kickstart negotiations. As the documentary record reveals, Iran ought to be praised for the supreme restraint and patience it has exercised in the face of these absurd machinations, wherein threats, sanctions, cyberattacks, and outright bombings are marketed as peace inducements.
The power wielded by the U.S. in certain areas has since grown significantly since the pre-revolutionary period, particularly in the sphere of economic warfare, otherwise known as international finance. Authors of a 2022 article in the American Journal of Sociology find that the financialization of U.S. warfare has greatly expanded its ability to instill submission to its commercial designs abroad. They argue that the policy “works like a virus by requiring infected corporate giants in high-risk countries to act as if they were U.S. legal persons and therefore to always follow U.S. law over other rules,” subordinating them to a U.S.-dominated “surveillance capitalism.” In the case of Iran, the U.S. began by targeting smaller, defenseless firms, then gradually enlarged its bullying operation to include several juggernauts of global capital. “[S]tarting with a few nondescript companies dealing with Iran’s shadow economy, now the largest European banks, the world’s largest telecom equipment providers, the world’s largest aircraft manufacturer, the world’s largest oil companies, and the world’s largest rolling stock manufacturers have all seen their inner rules reconfigured by U.S. sanctions law, forcing them to pull out of global markets if not complying with U.S. sanctions law.” Keeping Iran’s economy dependent on oil sales operating in an international market would therefore keep it in a realm in which the U.S. still wields tremendous leverage.
Much the way during the Cold War the USSR was the ubiquitous specter used to justify U.S. intervention throughout the world—invoking political and military links, both real and fabricated—Iran has been assigned a similar role in the Middle East, presented as a near omnipotent boogeyman that has implanted its links deep in Arab states. This presentation greatly benefits U.S.-Israeli efforts to expand its warmaking in a region still considered critical for international power. October 7, it can be argued, handed Israel its own 9/11—an act of terrorism so severe that it can implement its most wide-ranging contingency plans while above suspicion.
In 2009, Anthony Cordesman wrote that during previous, bloody sojourns in Gaza, dignified as “operations” in Israeli parlance, the IDF “did not go to war with plans to conduct a sustained occupation [of Gaza], to try to destroy Hamas or all of its forces, or to reintroduce the Palestinian Authority and Fatah, although such contingency plans and exercises may have existed.” The past 24 months reveal that they certainly did exist, and would be implemented if given an adequate pretext. Internal plans likely stretch back much further, but one of the early articulations came from dovish Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin, who famously admitted to reporters in 1992, “I wish the Gaza Strip would sink into the water, but I cannot find for it such a solution.” His extremist statement did not spare him from the bullets of an even more extreme assassin three years later, but the depth of the sentiment he expressed endured in Israeli politics across a wide spectrum. In July 2014, the ultra-right Knesset member Moshe Feiglin wrote a seven-point prescription for Gaza, which reads like an exact playbook of what Israel has implemented since October 7. After issuing one official “ultimatum,” Israel’s army will seek to destroy the “enemy population” of Gaza, allowing those who wish to leave an outlet into the Sinai, hence Israel’s current need to control the Rafah. “Sinai is not far from Gaza and they can leave. This will be the limit of Israel’s humanitarian efforts,” he asserts. “All the military and infrastructural targets will be attacked with no consideration for ‘human shields’ or ‘environmental damage,’” he continues, after which the IDF will oversee a complete siege of the enclave. Then, “the IDF will conquer the entire Gaza, using all the means necessary to minimize any harm to our soldiers, with no other considerations.” Occupied Gaza will finally be absorbed into Greater Israel, as it is “part of our Land and we will remain there forever,” also helping to ease the burgeoning housing crisis in Israel. Feiglin is confident that the few wretched Arabs that remain can be paid to leave, or accept the supremacy of their new Israeli wardens.
The Arab delegations assembled in Cairo know full well that their efforts amount to political theater. A trivial point, worth reiterating, the U.S. and Israel have not spent the last two years destroying Gaza to simply institute a ceasefire, allow in massive humanitarian aid, rid it—somehow—of Hamas, spend upwards of $100 billion to rebuild an entire civilization, and then return it to the Palestinians, all of whom are still cut off from the West Bank. No, the infinite credit line required for such an effort is earmarked to convert the area into another province of Israel. Capitalizing on the recent killing of six Israelis in Jerusalem, Smotrich also announced his plan to annex 82% of the West Bank, in the process slandering the Palestinian Authority with the same hysterical rhetoric typically reserved for Hamas. In other words, there are no more “good Arabs” anywhere, and Israel must exert its control directly. He added that “the villages from which the terrorists came should look like Rafah and Beit Hanoun,” i.e., completely flattened and emptied of its current residents, paving the way for Israeli seizure.
Soon, the Egyptians will come to realize that the only appropriate humanitarian act left is to begin accepting droves of hapless Palestinians through the Rafah. The refusal to comply with Israel’s ethnic cleansing will therefore be superseded by the need to ensure that all Gazans do not simply die off amidst the rubble of their former environs. September’s Israeli bombing of Doha, meant to murder more of Hamas’s leadership as it considered peace proposals, was yet another stark warning to negotiating parties: Try as you might, our plan is already in full swing. Qatar responded: “As has happened before, the Israelis sabotaged hopes for peace, further prolonging the war and complicating efforts to bring back the hostages.” Cairo would surely be next, pending U.S. willingness to completely scrap the 1978 Camp David Accords, but Israel’s alleged discovery of new tunnels underneath the Philadelphi Corridor have not proven a sufficient ploy. Given that the members allegedly killed in the attack had arrived in from Turkey, with whom Israel does not have a security treaty, Ankara should also be on high alert.
Breach of the Genocide Convention aside, the lesser crime of targeted assassination is hardly discussed. Six UN special rapporteurs condemned the Doha strike, saying it “violates the human right to life, the UN Charter prohibition on excessive use of force, and Qatar’s sovereignty.” In response to the killing of Saleh Al-Arouri just south of Beirut in January, two of the same UN special rapporteurs observed that, “Israel was not exercising self-defence because it presented no evidence that the victims were committing an armed attack on Israel from Lebanese territory,” a key requirement of the UN Charter. One would be hard-pressed to find an Israeli assassination that is not befitting of such a characterization.
Relief for Gazans
After the April 2024 murder of seven aid workers working with the World Central Kitchen, B’Tselem published a report entitled Manufacturing Famine: Israel is committing the war crime of starvation in the Gaza Strip, finding that Israel’s begrudging permission of paltry international aid into the enclave is “clearly too little, too late, and attests to Israel being chiefly responsible for the humanitarian crisis that has, since the war began about six months ago, spiraled into the catastrophe we are witnessing now.” Israel is waging war not only on Gaza’s physical infrastructure, having destroyed cement factories, religious institutions, schools, hospitals, agricultural land, and sewage treatment facilities, but on the future of the very civilization that occupies it. Systematic starvation, when employed as a method of war, is doubly devastating; it not only consumes its immediate victims, like the ill and the elderly, it also severely impairs the development of children, particularly in their first two years of life. As is well-known, half of Gaza is composed of children, ensuring that, long after the current assault has ceased, Palestinians will continue to mire in its hideous effects.
At the end of last February, for example, Israel made its first foray into overseeing direct aid administration in Gaza since the October 7th attacks, in a context Amnesty International characterized as an “already catastrophic humanitarian situation in the entire Gaza strip.” After escorting up to 30 aid trucks to the Nabulsi Roundabout, just southwest of Gaza City, “The events illustrate how a power vacuum in the Gaza Strip, particularly in its bombed-out biggest city in the north [Gaza City], has created a combustible mix of starving people, soldiers and militants that humanitarian experts and military analysts said was destined to blow up sooner or later.” Israel then decided to partake in the aid distribution process more directly, but not without its patented murderous touch, somewhat placating citizens who had worked to disrupt the dispatch of any aid. Instead, crowds of recipients were shot at indiscriminately, and aid workers, by mere virtue of aiding the intended prey, truly court their own demise. “The U.N. and international aid groups have scaled back their missions to the north in recent weeks because of the intensity of the conflict and widespread lawlessness,” The Wall Street Journal reported, resulting in conditions that resemble an archetypal Haitian disaster. More recently, when hospital beds, medical equipment, and medicines dried up, parallels were drawn to famines seen in Darfur and Somalia.
[Content truncated due to length…]
From CounterPunch.org via this RSS feed