Has anyone noticed that news stories have gotten shorter and pithier over the past few decades, sometimes seeming like summaries of what you used to peruse? In spite of that, huge numbers of people are relying on large language model (LLM) “AI” tools to get their news in the form of summaries. According to a study by the BBC and European Broadcasting Union, 47% of people find news summaries helpful. Over a third of Britons say they trust LLM summaries, and they probably ought not to, according to the beeb and co.
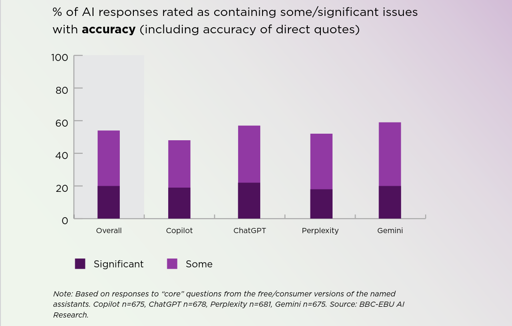
It’s a problem we’ve discussed before: as OpenAI researchers themselves admit, hallucinations are unavoidable. This more recent BBC-led study took a microscope to LLM summaries in particular, to find out how often and how badly they were tainted by hallucination.
Not all of those errors were considered a big deal, but in 20% of cases (on average) there were “major issues”–though that’s more-or-less independent of which model was being used. If there’s good news here, it’s that those numbers are better than they were when the beeb last performed this exercise earlier in the year. The whole report is worth reading if you’re a toaster-lover interested in the state of the art. (Especially if you want to see if this human-produced summary works better than an LLM-derived one.) If you’re a luddite, by contrast, you can rest easy that your instincts not to trust clanks remains reasonable… for now.
Either way, for the moment, it might be best to restrict the LLM to game dialog, and leave the news to totally-trustworthy humans who never err.
From Blog – Hackaday via this RSS feed